Crowns And Bridges
Crowns and bridges are common dental restorations used to restore damaged or missing teeth. Both are designed to improve the function and appearance of your teeth, but they serve different purposes and are used in different situations. Here’s a detailed overview of crowns and bridges:
Dental Crowns
Purpose:
- Protection: To cover and protect a tooth that has been weakened by decay, large fillings, or fractures.
- Restoration: To restore the shape, size, and strength of a tooth after a root canal or significant damage.
- Aesthetics: To improve the appearance of a tooth that is discolored, misshapen, or otherwise unattractive.
Types of Crowns:
1. Porcelain Crowns:
- Material: Made of high-quality ceramic material.
- Advantages: Offers a natural look, making it ideal for front teeth where aesthetics are a concern.
- Disadvantages: May not be as durable as metal crowns for back teeth.
2. Metal Crowns:
- Material: Made of gold, platinum, or other metal alloys.
- Advantages: Highly durable and resistant to wear, making them suitable for back teeth that endure heavy chewing forces.
- Disadvantages: Less aesthetically pleasing, as they do not match the natural color of teeth.
3. Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal Crowns:
- Material: A metal base covered with a layer of porcelain.
- Advantages: Combines the strength of metal with the natural appearance of porcelain.
- Disadvantages: May have a visible metal line at the gumline, and can sometimes cause more wear on adjacent teeth.
4. All-Ceramic or All-Resin Crowns:
- Material: Made entirely of ceramic or resin.
- Advantages: Provides a natural appearance and is a good choice for patients with metal allergies.
- Disadvantages: May not be as strong as metal crowns and may wear down faster over time.
Procedure:
- Preparation: The tooth is shaped to accommodate the crown. This often involves removing some of the tooth’s structure.
- Impression: An impression of the prepared tooth is taken to create a custom crown.
- Temporary Crown: A temporary crown may be placed while the permanent crown is being fabricated.
- Placement: Once the permanent crown is ready, it is placed and cemented onto the prepared tooth.
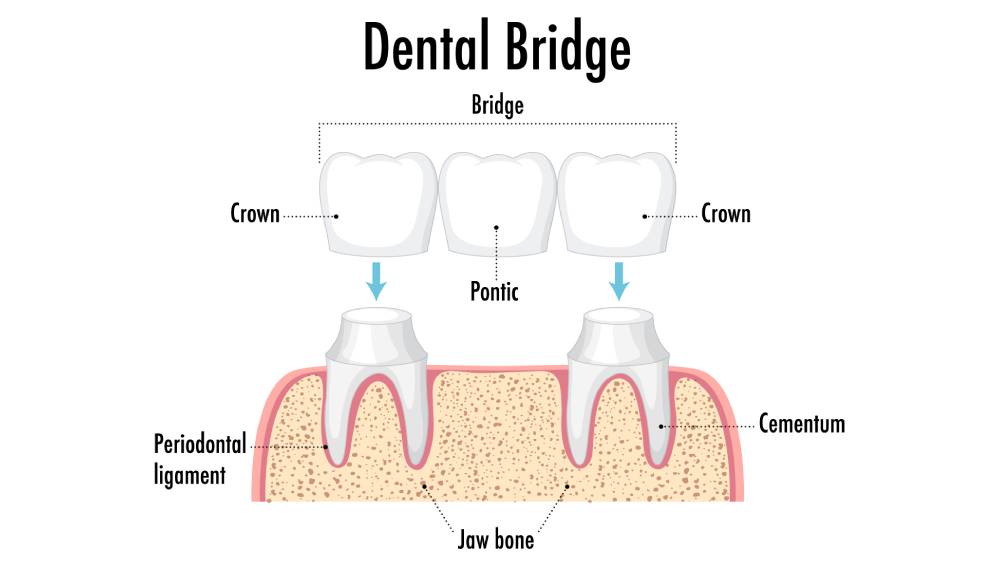
Dental Bridges
Purpose:
To Replace Missing Teeth: Bridges are used to fill the gap created by one or more missing teeth.
To Restore Function: Helps in restoring normal biting and chewing functions.
To Improve Appearance: Bridges help in maintaining the natural shape of the face and improving the smile.
Types of Bridge:
1. Traditional Bridge:
- Design: Consists of one or more artificial teeth (pontics) held in place by crowns on the adjacent teeth (abutment teeth).
- Advantages: Common and effective solution for replacing missing teeth.
- Disadvantages: Requires the adjacent teeth to be crowned, which involves the removal of healthy tooth structure.
2. Cantilever Bridge:
- Design: A bridge that is anchored to a single abutment tooth, extending over the gap.
- Advantages: Useful when there is only one adjacent tooth available for support.
- Disadvantages: Less stable than traditional bridges and may not be suitable for large gaps.
3. Maryland Bridge (Resin-Bonded Bridge)::
- Design: Consists of a metal or ceramic framework with wings that are bonded to the back of the adjacent teeth.
- Advantages: Less invasive, preserves more of the natural tooth structure, and is often used for front teeth.
- Disadvantages: May not be as durable for back teeth or for larger gaps.
4. Implant-Supported Bridge:
- Design: Supported by dental implants rather than natural teeth. Implants are surgically placed in the jawbone and used to anchor the bridge.
- Advantages: Provides a stable and durable solution without affecting adjacent teeth.
- Disadvantages: Requires surgery and may be more expensive than other types of bridges.
Procedure:
- Preparation: Adjacent teeth are prepared for crowns if using a traditional bridge, or implants are placed if using an implant-supported bridge.
- Impression: Impressions of the teeth or implants are taken to create the bridge.
- Temporary
- Placement: The permanent bridge is placed and adjusted for fit and comfort before being cemented or bonded into place.